Proxy War

New escalation in regional conflict
| OpinionThe killing of three American soldiers in Jordan by pro-Iran militias via UAV strikes initiated …
-
Opinion
New escalation in regional conflict
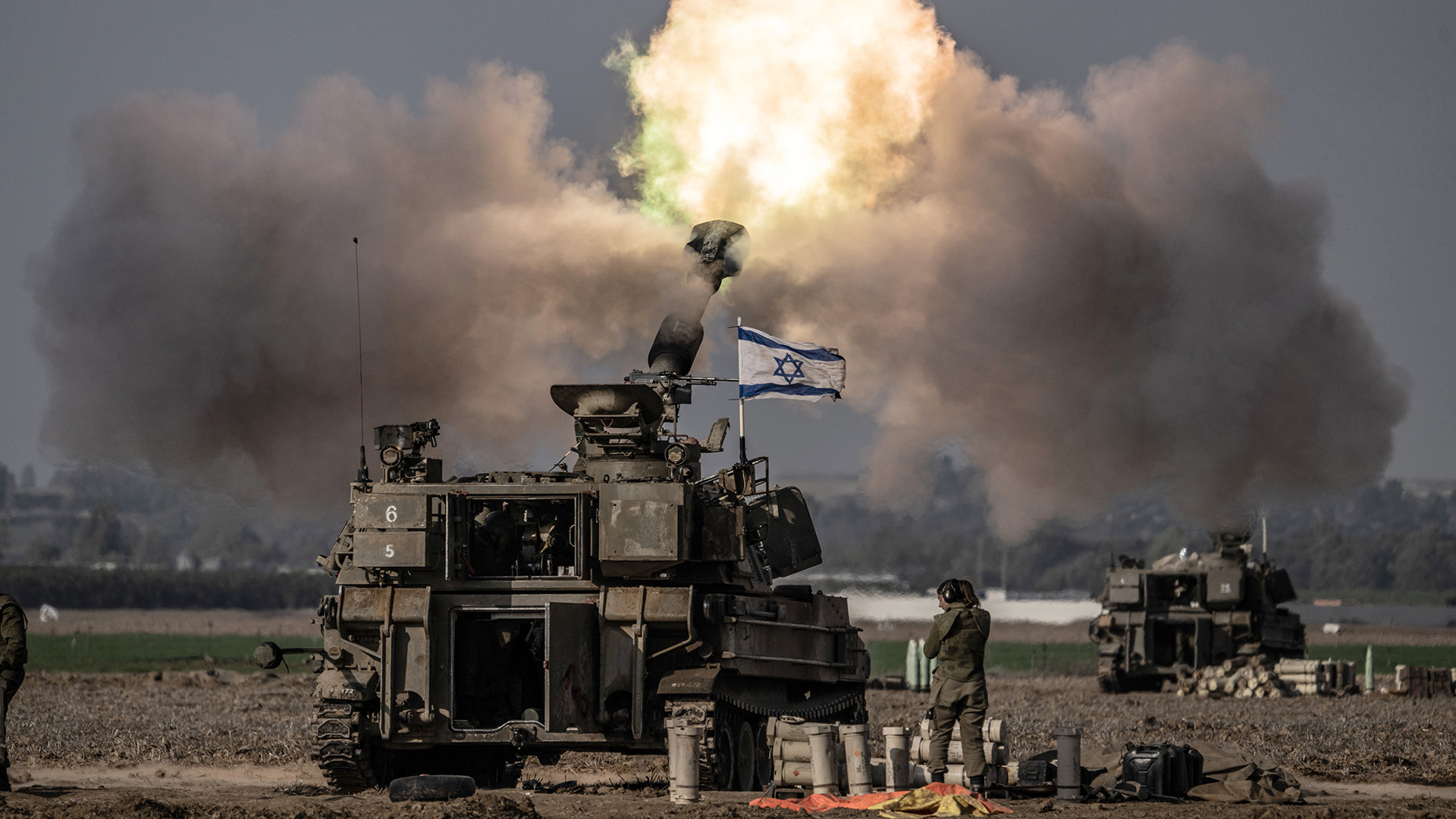
By Kadir ÜstünThe killing of three American soldiers in Jordan by pro-Iran militias via UAV strikes initiated a new escalation in the escalating regional conflict. Since October 7th, concerns about regional warfare seemed obsolete. We previously noted Israeli Prime Minister Netanyahu's attempt to expand the Gaza conflict regionally and entangle the US in conflict with Iran. The Jordan attack partially succeeded in these efforts. Over the past week, the US conducted military operations in the region, signaling a response.
-
Opinion
Complex dynamics of Türkiye-Iran relations
By Murat YeşiltaşTraditionally, Türkiye-Iran relations have been defined by a mix of competition and cooperation. Sharing a long land border and possessing a multidimensional historical depth, numerous dynamics simultaneously affect the relationship between the two countries.
-
Opinion
Is Iran strengthening or becoming isolated?
By Burhanettin DuranAgainst the backdrop of Israel's massacre in Gaza, attention has been shifting to Iran. Following the bombardment of the Houthis by the United States and the United Kingdom for disrupting commercial shipping in the Red Sea, Iran and Pakistan experienced an escalation, with both sides firing missiles over terrorism. Moreover, Israel killed five members of the Revolutionary Guards Corps in Damascus last weekend, resuming its past operations against the Iranian presence in Syria. The seeming purpose of such strikes is to stop Iran from sending military aid to the Axis of Resistance – namely Hezbollah and Hamas. More important, however, is Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu's commitment to ensuring the Israeli-Palestinian conflict's regionwide spillover – which contradicts the Biden administration.
Bu Konuda Daha Fazla
-
Aren’t we already in the midst of a regional...
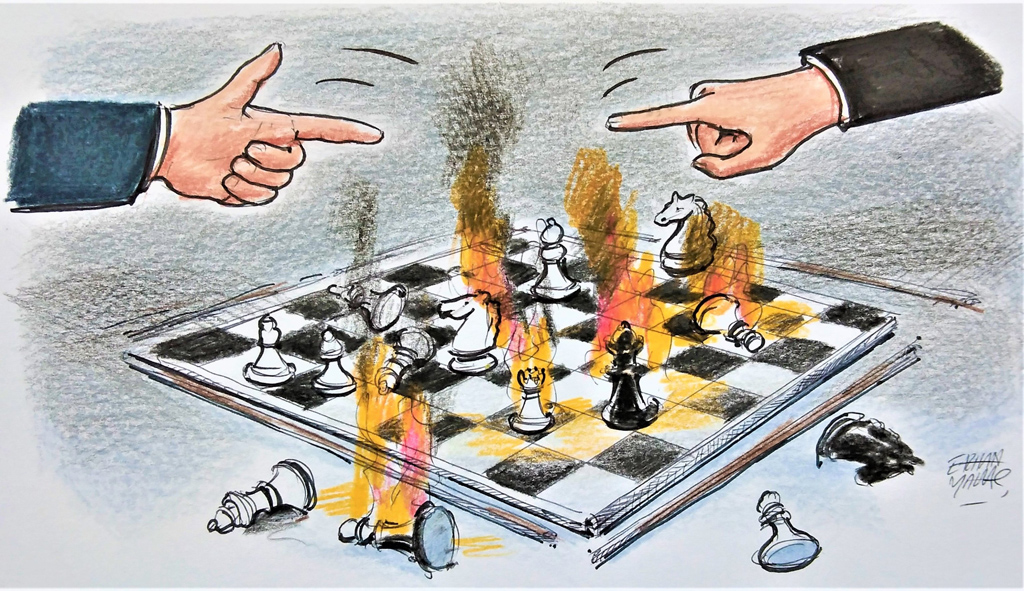
By Kadir ÜstünWe're talking about the possibility of Israel's attacks on Gaza triggering a regional war after October 7. Recent developments actually indicate that we are already in the midst of a regional war. However, the fluctuating intensity of such conflicts and the fact that the parties involved are not always clearly defined make it difficult to label it as a regional war. The evolution of warfare between countries, occurring in complex ways across different arenas and activating the capacities of various parties, has made traditional, all-encompassing wars increasingly rare. Many countries now prefer proxy wars due to their lower cost, lower risk, and deniability.
-
Who benefits from controlled proxy conflict?
By Burhanettin DuranThe Middle East rang in the new year with assassinations and terror attacks. Saleh al-Arouri, the deputy leader of Hamas' political bureau, was assassinated in Beirut last Tuesday. The following day, two bombings in Kirman, Iran (for which Daesh has claimed responsibility) killed 103 people. As those attacks shifted everyone’s attention to Israel, Iran and Hezbollah pledged to exact “revenge and a heavy price.”
-
Sudanese crisis: A new front of ‘preventive proxy war’
By Muhittin AtamanConsidering the devastating effects of new-generation weapons, global powers cannot launch direct wars against each other. Therefore, they prefer to engage in indirect battles, as the two superpowers, the United States and the Soviet Union, did during the Cold War. Their proxies fight each other; they control the tide of the war from behind closed doors by procuring military equipment and by providing economic and financial assistance to wage war.
-
Arab Spring: A flashback to past 10 years
By Burhanettin DuranThe wave of democratization, which began with the Jasmine Revolution in Tunisia, took down the authoritarian leaders of Egypt, Libya and Yemen. Whereas the uprising in Bahrain was crushed thanks to Saudi Arabia’s military intervention, Iran and Russia ensured the survival of Bashar Assad’s regime in Syria.
-
Time for the PKK and its sponsors to admit...
By Burhanettin DuranThe PKK/YPG threat in the region is far from over, but the group's nationalist project — the so-called 'cantons' — are now dead in the water